Stack Implementation in C++
Course: Data Structures
Using Arrays with push(), pop(), and display()
Presented by: Nayan Kumar Ray & Heridoy Chowdhury
Introduction to Stack
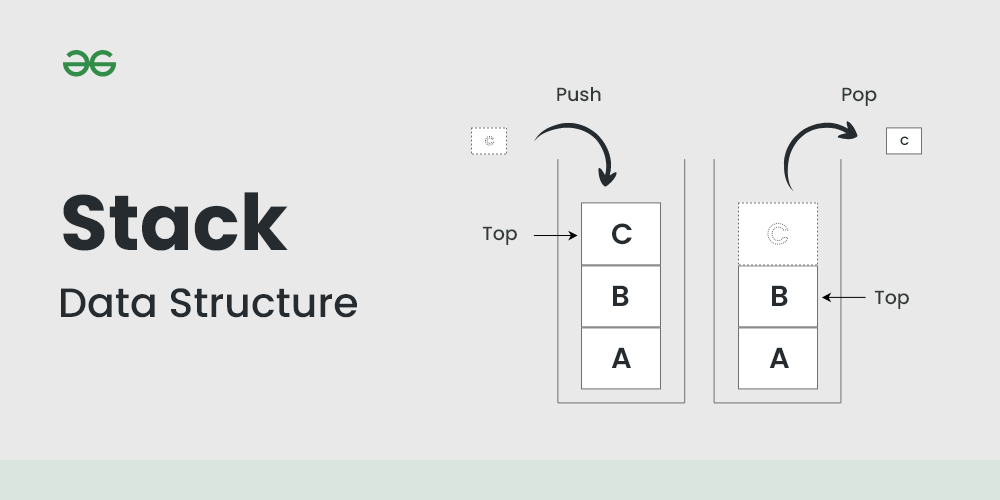
Stack Operations
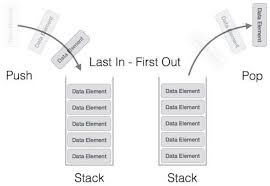
Stack Implementation
#include <iostream> #define MAX 5
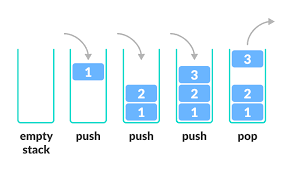
Stack Class Definition
class Stack {
int top;
int arr[MAX];
public:
Stack() { top = -1; }
};
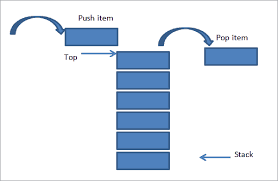
Push Operation
void push(int value) {
if (top >= MAX - 1) {
std::cout << "Stack Overflow\n";
return;
}
arr[++top] = value;
}
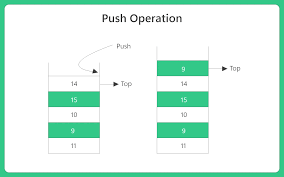
Pop Operation
void pop() {
if (top < 0) {
std::cout << "Stack Underflow\n";
return;
}
std::cout << arr[top--] << " popped from stack\n";
}
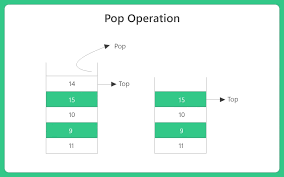
Display Function
void display() {
if (top < 0) {
std::cout << "Stack is empty\n";
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
std::cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
Main Function
int main() {
Stack s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
s.display();
s.pop();
s.display();
return 0;
}
Output Example
10 pushed into stack 20 pushed into stack 30 pushed into stack Stack elements: 30 20 10 30 popped from stack Stack elements: 20 10
Explanation for Lab Exam
#include <iostream>
#define MAX 100
using namespace std;
class Stack {
private:
int arr[MAX];
int top;
public:
Stack() { top = -1; }
void push(int value) {
if (top >= MAX - 1) {
cout << "Stack Overflow!" << endl;
return;
}
arr[++top] = value;
}
int pop() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack Underflow!" << endl;
return -1;
}
return arr[top--];
}
void display() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Stack s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
s.display();
cout << "Popped: " << s.pop() << endl;
s.display();
return 0;
}